Nvidia has announced its next generation of AI hardware at the GPU Technology Conference (GTC) 2024. The highlight of the event is the announcement of the Blackwell B200 GPU, boasting significant performance improvements and efficiency gains over its predecessor, the H100. Nvidia also unveiled the Grace CPU Superchip, the GB200, which combines two B200 GPUs with a single Grace CPU to deliver even more powerful AI processing capabilities.
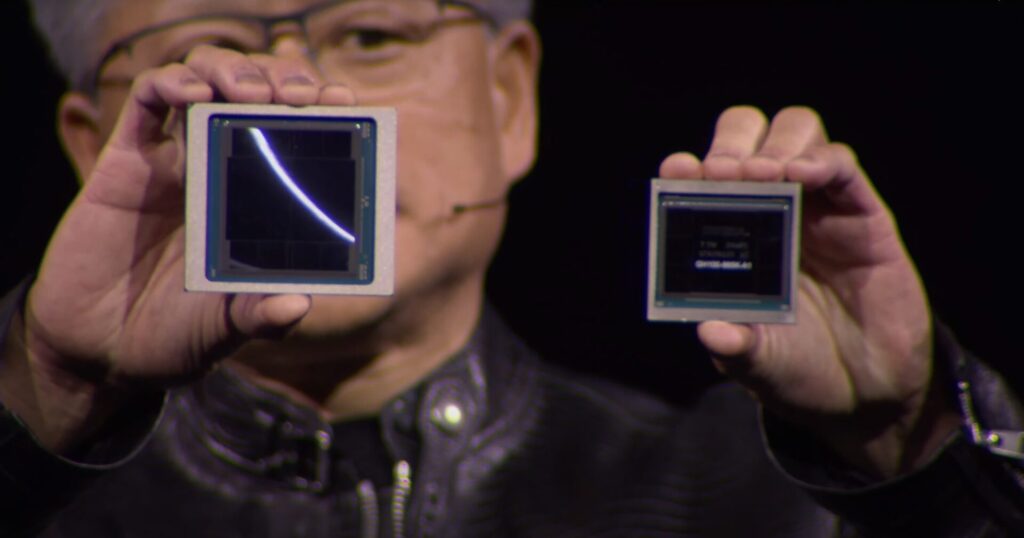
The B200 GPU is manufactured on a custom 4nm TSMC process and it packs a staggering 208 billion transistors. This translates to up to 20 petaflops of FP4 horsepower, a significant leap from the H100.
Nvidia claims the B200 achieves this performance while also being substantially more efficient. The company states that the B200 “reduces cost and energy consumption by up to 25x” compared to the H100. This efficiency improvement is crucial for large-scale AI deployments, where power consumption can be a major cost factor.
One key improvement in the B200 is the second-generation transformer engine. This engine utilizes four bits per neuron for computations instead of the eight bits used in the H100. This approach effectively doubles the compute and model size that can be handled by the B200 while maintaining performance.
Grace CPU Superchip

Nvidia’s ambition extends beyond the B200 with the introduction of the Grace CPU Superchip, the GB200. This innovative design combines two B200 GPUs with a single Grace CPU on a single board. This configuration offers a significant performance boost for specific AI workloads, particularly large language model (LLM) inference.
According to Nvidia, the GB200 delivers 30 times the performance for LLM inference compared to a single H100. As an example, Nvidia claims that training a 1.8 trillion parameter model, which previously would have required 8,000 Hopper GPUs and 15 megawatts of power, can now be accomplished with just 2,000 Blackwell GPUs consuming only four megawatts.
For benchmarks involving smaller LLMs, the GB200 still offers a significant advantage. Nvidia reports a seven-fold performance improvement over the H100 on a GPT-3 LLM benchmark with 175 billion parameters. Additionally, training speed is said to be quadrupled compared to the H100.
Scalability and Cloud Adoption
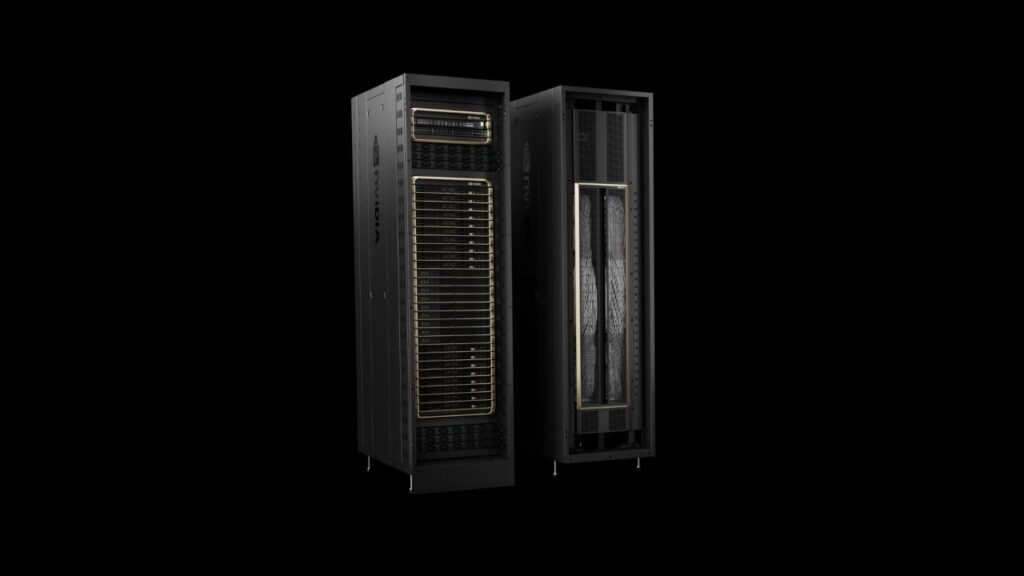
Nvidia is preparing for large-scale adoption of the B200 and GB200 architectures. The company offers various configurations, including the GB200 NVL72, which integrates 36 CPUs and 72 GPUs into a single liquid-cooled rack. This single rack delivers a remarkable 720 petaflops of AI training performance and a mind-boggling 1.4 exaflops of inference performance.
Nvidia has secured partnerships with major cloud providers like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Oracle, who plan to offer the NVL72 racks as part of their cloud service offerings.
While the focus of GTC 2024 is on AI advancements, the Blackwell architecture is expected to form the foundation for the upcoming RTX 50-series lineup of desktop graphics cards.


























![HATASU Launches HATASUKILIG treats and deals! [PR Banner] HATASUKILIG Feb Ibig Campaign ()](https://jamonline.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/PR-Banner-HATASUKILIG-Feb-Ibig-Campaign-1-218x150.jpeg)




